This is a text-only version of the following page on https://raymii.org:
---
Title : nameConstraints on your Self Signed Root CA in Kubernetes with cert-manager
Author : Remy van Elst
Date : 17-07-2024 23:22
URL : https://raymii.org/s/tutorials/nameConstraints_on_your_Self_Signed_Root_CA_in_Kubernetes_with_cert_manager.html
Format : Markdown/HTML
---
If you have [set up a Self Signed Root CA](/s/tutorials/Self_signed_Root_CA_in_Kubernetes_with_k3s_cert-manager_and_traefik.html) for your local Kubernetes Cluster and have trusted the Root Certificate, you are at risk if the key is compromised. If the key is stolen, it can be used to create trusted certificates for everything. Luckily there is something we can do, using `nameConstraints` to limit the scope of the Root Certificate to, in our case, a single domain (`k3s.homelab.mydomain.org`). This means that if your key would be compromised, it would only be able to issue certificates for anything under that domain, not your bank for example.
Recently I removed all Google Ads from this site due to their invasive tracking, as well as Google Analytics. Please, if you found this content useful, consider a small donation using any of the options below. It means the world to me if you show your appreciation and you'll help pay the server costs:
GitHub Sponsorship
PCBWay referral link (You get $5, I get $20 after you've placed an order)
Digital Ocea referral link ($200 credit for 60 days. Spend $25 after your credit expires and I'll get $25!)
[RFC 5280](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5280) provides for something called
`Name Constraints`, which allow an X.509 CA to have a scope limited to
certain names, including the parent domains of the certificates issued by the
CA. For example, a host constraint of `.example.com` allows the CA to issue
certificates for anything under `.example.com`, but not any other host. For
other hosts, clients will fail to validate the chain. [More info here]
(https://web.archive.org/web/20240415204151/http://www.pkiglobe.org/name_constraints.html).
We'll end up with the following error for certificates not under your homelab domain name:
Kubernetes `cert-manager` has experimental support for `nameConstraints`,
quoting [the documentation]
(https://cert-manager.io/docs/reference/api-docs/#cert-manager.io/v1.CertificateSpec):
> This is an Alpha Feature and is only enabled with the
`--feature-gates=NameConstraints=true` option set on both the `controller`
and `webhook` components.
More info on [feature gates](https://web.archive.org/web/20240717192139/https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/configuring-components/)
can be found [here](https://web.archive.org/web/20240717192139/https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/configuring-components/):
> Alpha: feature is not yet stable and might be removed or changed in the
future. Alpha features are disabled by default and need to be explicitly
enabled by the user (to test the feature).
### Configure the feature gate on cert-manager
If you have followed my [previous guide on setting up a Self Signed Root CA](/s/tutorials/Self_signed_Root_CA_in_Kubernetes_with_k3s_cert-manager_and_traefik.html)
you will already have a working setup for `cert-manager` via the Helm chart.
If not, go follow that guide.
If you have a different installation method, check [here](https://web.archive.org/web/20240717192139/https://cert-manager.io/docs/installation/configuring-components/)
for more info on configuring feature gates.
You have append the following two parameters to the Helm install command to
enable the feature gate for `NameConstraints`:
--set webhook.featureGates="NameConstraints=true" \
--set featureGates="NameConstraints=true"
The full Helm install command then becomes:
helm upgrade --install \
cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--create-namespace \
--version v1.15.1 \
--set crds.enabled=true \
--set webhook.timeoutSeconds=4 \
--set replicaCount=2 \
--set podDisruptionBudget.enabled=true \
--set podDisruptionBudget.minAvailable=1 \
--set webhook.featureGates="NameConstraints=true" \
--set featureGates="NameConstraints=true"
You can also choose to create a `values.yaml` file for this Helm install. All
possible options can be found [here](https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/cert-manager/cert-manager).
### Adding nameConstraints to a Root Certificate
We have to add the following [to the `spec`](https://web.archive.org/web/20240717191851/https://cert-manager.io/docs/reference/api-docs/#cert-manager.io/v1.CertificateSpec)
of our Root CA:
vim spnw-root-ca.yaml
Add under `spec`:
nameConstraints:
critical: true
permitted:
dnsDomains:
- k3s.homelab.mydomain.org
Repeat this for `spnw-intermediate-ca1.yaml`
You have to delete the current CA and corresponding secret first:
kubectl -n cert-manager delete secret spnw-root-ca-secret
kubectl -n cert-manager delete -f spnw-root-ca.yaml
kubectl -n cert-manager delete -f spnw-intermediate-ca1.yaml
Apply the changes:
kubectl -n cert-manager apply -f .
If you have not enabled the feature gate you will receive an error:
for: "spnw-root-ca.yaml": error when patching "spnw-root-ca.yaml":
admission webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io" denied the request:
spec.nameConstraints: Forbidden: feature gate NameConstraints must be
enabled
You can now get the `Secret` and check to see if the `nameConstraint` is present:
kubectl get secret spnw-root-ca-secret -n cert-manager -o json |
jq -r '.data["tls.crt"]' | base64 --decode | openssl x509 -noout -text
Output:
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
[...]
X509v3 extensions:
[...]
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:TRUE
X509v3 Name Constraints: critical
Permitted:
DNS:k3s.homelab.mydomain.org
The following part:
X509v3 Name Constraints: critical
Permitted:
DNS:k3s.homelab.mydomain.org
means that any certificate issued for a hostname not within
`k3s.homelab.mydomain.org` will fail to validate, which is exactly what we
want.
You must remove the old certificate from your trusted root store (Windows `certmgr.msc` or Firefox)
and add this new certificate. Then you must re-issue all certificates from services you have
already issued.
### Validating `nameConstraints`
To test the constraint, I've set up a wildcard DNS domain to
`k8s.homelab.mydomain.org` (note `k8s` instead of `k3s`) and issued a
certificate for my `echoapp` test service. Using OpenSSL to validate that
fails with a `permitted subtree violation`, which is the exact error for this
failure, the domain does not match the `nameConstraints`:
openssl verify -CAfile <(kubectl -n cert-manager get secret spnw-root-ca-secret -o jsonpath='{.data.tls\.crt}' | base64 --decode) -untrusted <(kubectl -n cert-manager get secret spnw-intermediate-ca1-secret -o jsonpath='{.data.tls\.crt}' | base64 --decode) <(kubectl -n echoapp get secret echo-cert -o jsonpath='{.data.tls\.crt}' | base64 --decode)
Output:
CN = echo.k8s.homelab.mydomain.org
error 47 at 0 depth lookup: permitted subtree violation
error /dev/fd/61: verification failed
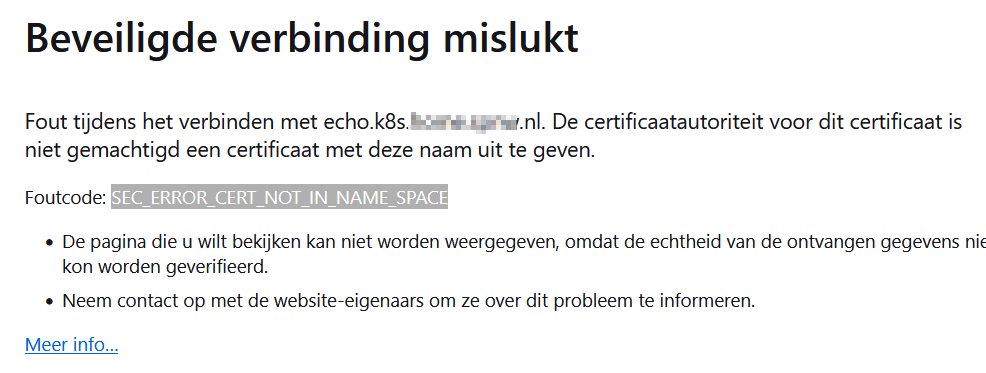
Firefox also complains with an `SEC_ERROR_CERT_NOT_IN_NAME_SPACE` error:

If you manually want to set up `nameConstraints` with `openssl`, [this is a
good guide]
(https://web.archive.org/web/20240717202700/https://systemoverlord.com/2020/06/14/private-ca-with-x-509-name-constraints.html).
---
License:
All the text on this website is free as in freedom unless stated otherwise.
This means you can use it in any way you want, you can copy it, change it
the way you like and republish it, as long as you release the (modified)
content under the same license to give others the same freedoms you've got
and place my name and a link to this site with the article as source.
This site uses Google Analytics for statistics and Google Adwords for
advertisements. You are tracked and Google knows everything about you.
Use an adblocker like ublock-origin if you don't want it.
All the code on this website is licensed under the GNU GPL v3 license
unless already licensed under a license which does not allows this form
of licensing or if another license is stated on that page / in that software:
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see .
Just to be clear, the information on this website is for meant for educational
purposes and you use it at your own risk. I do not take responsibility if you
screw something up. Use common sense, do not 'rm -rf /' as root for example.
If you have any questions then do not hesitate to contact me.
See https://raymii.org/s/static/About.html for details.